Documentation
CloudBasic:
- What is CloudBasic:
- Most common scenarios:
- Using CloudBasic:
- Prerequisites
- Limitations
- Supported MS SQL Server Versions
- Deployment Guide (PDF)
- Release Notes
- Get Started - Configure Multi-AZ or Multi-AR with Readable Replicas
- SQL Server to SQL Server Replication
- SQL Server to Redshift
- SQL Server to S3 Data Lake
- Monitor a Continuous Copy Relationship
- Promote RDS/SQL Server Read-Replica to Primary
- Terminate a Continuous Copy Relationship
- Logs and Errors
- Warnings
- How To Upgrade
- Updating your version
- CloudBasic advanced features:
- Working in AWS:
- RDS Assemblies Activation Test
- RDS/SQL Server User Management
- RDS/SQL Server Backup and restore from/to S3
- RDS/SQL Server Snapshot-Restore
- VPN/VPC - Replication over VPN/VPC
- Compare Instance Types (Features & Support Details)
- How To Extend the Default Data Storage
- Attach IAM Role to EC2 and Redshift Cluster
- Deployment guide:
- Additional topics:
API Documentation:
- Default API Configuration
- Instance Management:
- User Management:
- Replication Management:
- CreateReplication
- CreateAllReplication
- GetReplicationsList
- ReplicationStatus
- AlterReplication
- DeleteReplication
- StartReplicationService
- StopReplicationService
- AnalyzeReplication
- CreateRedshiftReplication
- AlterRedshiftReplication
- DeleteRedshiftReplication
- CreateS3Replication
- AlterS3Replication
- DeleteS3Replication
- GetLogs
- RebuildDbReplicaIndexes
- RebuildDbReplicaIndexesStatus
- ReseedTable
- ReseedTableStatus
- Multi-AZ HA Cluster Management:
- Lambda/node.js Example:
- Disaster Recovery & No-Downtime Migration Management
- Service Management:
Limitations
1. Applicable to the Disaster Recovery (DR) and migration use cases: DR database replica statistics (optimized query execution plans/DTA) are not maintained by the replication job. You are responsible to maintain execution plans/statistics. Otherwise in case of a DR event, the newly promoted to primary database server might perform poorly, until statistics are rebuilt.
The following DTA (Database Engine Tuning Advisor) objects are not replicated:
| Object type | Default object prefixes |
| Indexes | _dta_index_ |
| Statistics | _dta_stat_ |
| Views | _dta_mv_ |
| Partition functions | _dta_pf_ |
| Partition schemes | _dta_ps_ |
Note: if to compare number of objects in source and replica databases manually, exclude _dta objects, i.e. select count(*) from sys.indexes where name not like '%dta_index%'
2. Tables with Primary Keys (PKs) of type TimeStamp and tables of type FileTable are seeded but not tracked for changes real-time. For those tables the work around is to add those tables to a schedule to reseed tables (a seamless automatic process, but not a real-time solution). TimeStamp column values are not replicated, instead a new unique value is generated on the replica table upon insert/update by SQL Server. (Note: TimeStamp columns do not contain values directly relating to time, it simply is a number which is updated whenever a value in that record is. TimeStamp values are guaranteed to be unique within a database.)
3. Near Real-Time replication of tables without Primary Key is supported, but need to select CDC (Change Data Capture) under [Advanced] options in UI during initial job configuration (specify CDC in API call parameters if creating new jobs over API). See prerequisites for more information.
The easiest way to to determine if any of the above limitations apply, is to launch a trial CloudBasix instance, initiate a test replication(s).
Alternatively, manually execute Limitations Assessment Scripts against each database, and if necessary, reach out to Support for help with interpreting results.
4. Table truncate when the replication job is configured with CDC (Change Data Capture) is supported, but integration with CloudBasix API is required. Contact Support for more information.
5. Table partition truncate and partition switch are supported operations, but integration with CloudBasix API is required. See prerequisites or contact support for more information.
6. Windows/Active Directory logins (user accounts) are not replicated.
7. MSSQL Server level logins/users (along with roles) are replicated, however for security reasons random passwords are assigned. Passwords need to be manually reset on the replica SQL Server after the initial database replication seeding completes. Password changes are also not automatically replicated as part of the schema replication process.
Justification: CloudBasix is designed to be lightweight and to handle MSSQL Server continuous replication over TCP/IP and to work in cross-region (over VPN or data encrypted in transit SSL connections), cross-aws-accounts (data/DR artifacts are stored in multiple AWS accounts, account level security breach would not affect business continuity), on-premise to AWS RDS or EC2 MSSQL Server, and even InterCloud (AzureSQL-AW RDS, AWS RDS-Google Cloud SQL etc) replication scenarios.
8. Ambiguous Schema Changes:
Note: As of version 12.319, handling of ambiguous schema changes (see below definition) is subject to automation via activating of automatic table reseed upon detection of an ambiguous schema change (see job setting [ ] Reseed table(s) when ambiguous schema change is detected, if table record count less then [row count])
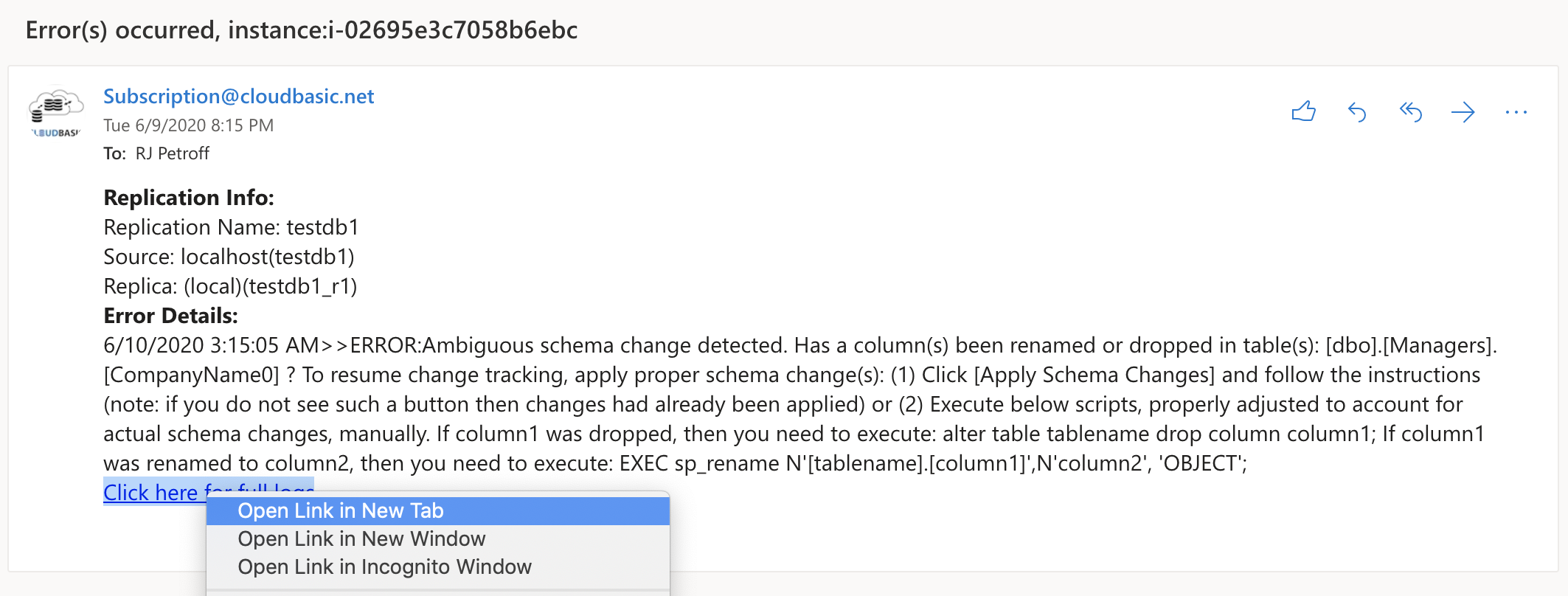
By design, for security reasons (default use case is DR), complex cases of multiple dropped or renamed table columns might not be automatically replicated in certain rare complex cases (user approval is required if the case is determined to be ambiguous) as part of the continuous schema replication process. Complex DB schema changes are usually part of planned releases, and the semi-automatic handling of those rare ambiguous cases of schema change tracking is handled as part of the planned release rolls out. In case of complex cases of multiple dropped or renamed column(s) the following ambiguous schema change detected error notification will be generated (and reported in runtime logs for each change tracking process run):
If follow the link in the emailed notification, will open respective error logs screen, where a button [Apply Schema Changes] ([Guide Me] in 12.82 and earlier versions) will be enabled:
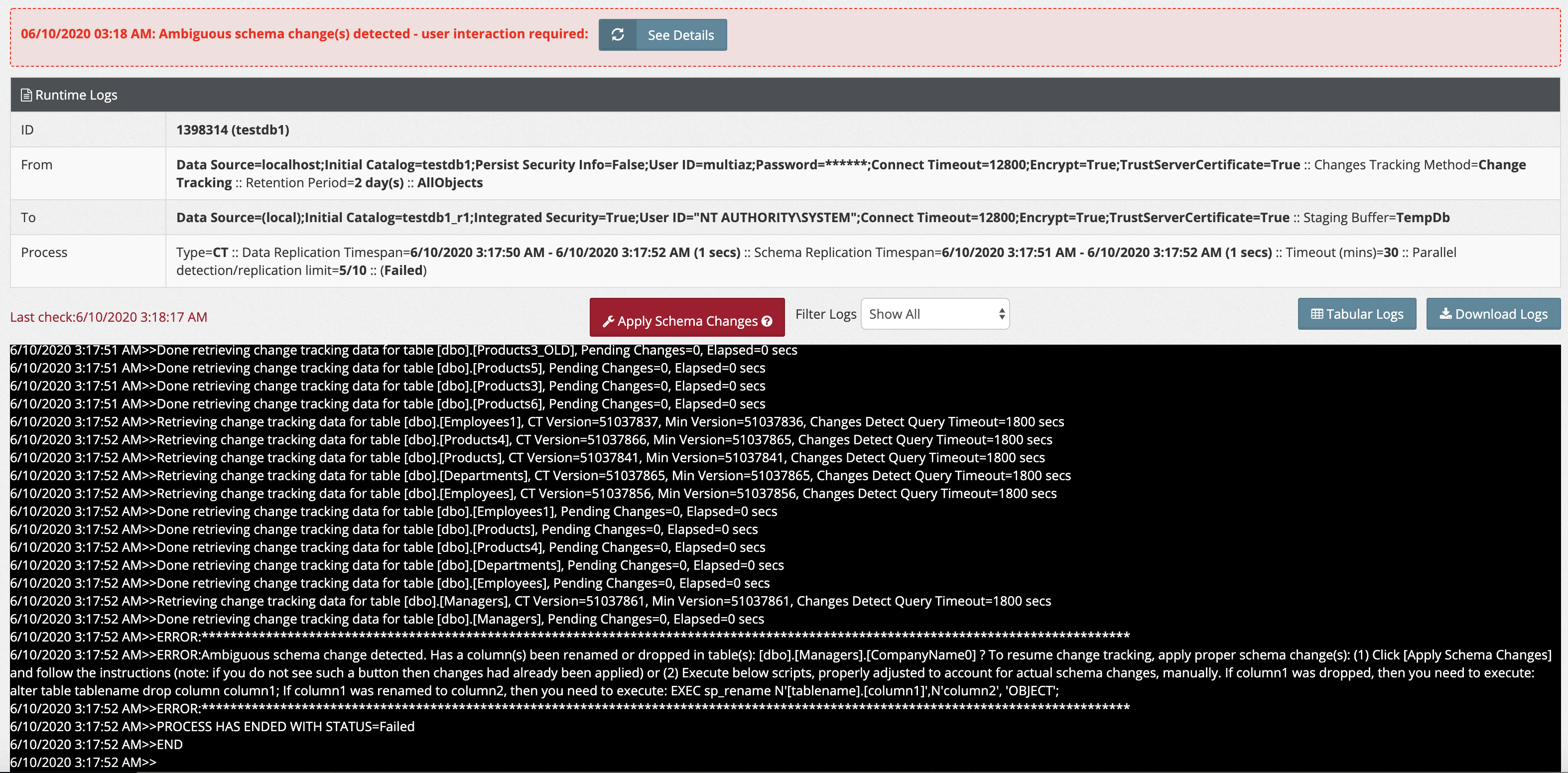
The following will be reported in runtime logs:
>>ERROR:Ambiguous schema change detected. A column(s) been renamed or dropped in table(s): [dbo].[Managers].CompanyName2, [dbo].[Managers].CompanyName3 ? To resume change tracking, apply proper schema change(s): (1) Click [Apply Schema Changes] button and follow the instructions (note: if you do not see such a button then changes had already been applied) or (2) Execute below scripts, properly adjusted to account for actual schema changes, manually: If column1 was dropped, then you need to execute: alter table tablename drop column column1; (Applicable to redshift replications only): On the Redshift side, you need to execute 2 statements: (1) alter table tablename drop column column1 (2) alter table tablename_stage drop column column1 If column1 was renamed to column2, then you need to execute: EXEC sp_rename N'[tablename].[column1]',N'column2', 'OBJECT'; (Applicable to redshift replications only): On the Redshift side, you need to execute 2 statements: (1) alter table tablename rename column column1 to column2 (2) alter table tablename_stage rename column column1 to column2
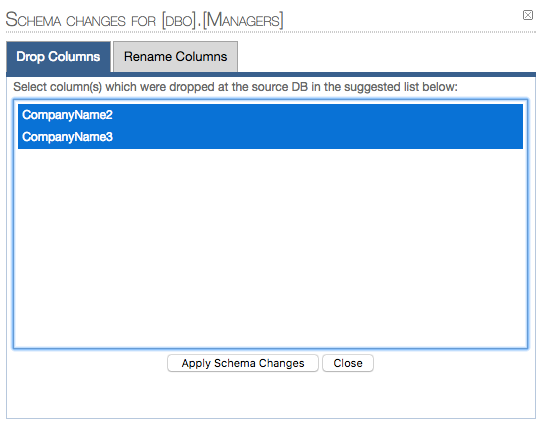
When you click the [Apply Schema Changes] button ([Guide Me] in 12.82 and earlier versions), you will land on an interactive wizard which will allow you to drop and/or rename columns without the need to manually execute alter queries against the staging data store and, if applicable to the replication type, against redshift:
DROP COLUMNS:
1.1 Selected columns to be dropped:

RENAME COLUMNS:
2.1 Map columns to be renamed (1 pair at a time - if more than 1 columns are renamed):
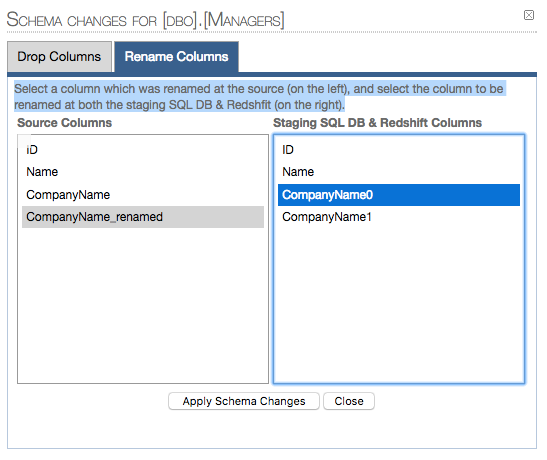
2.2 Renamed column confirmation:
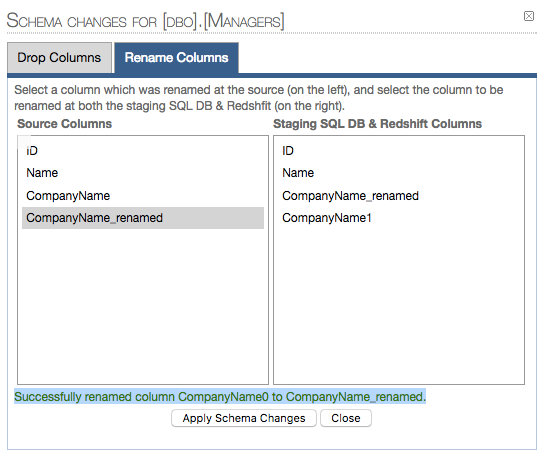
9.Temporal tables replication handling limitations:
9.1 Version 13.0 and above:
Temporal table schemas and data are replicated as part of the initial seeding (temporal tables are seeding after all primary data tables are seeded). After transitoning to ongoing tracking of changes, temporal tables are not tracked for changes. Ongoing changes are registered into temporal tables, maintained by the replica SQL Server.
Important (applicable to both Change Data Capture (CDC) and Change Tracking selected method for tracking of changes):
If a temporal table field value is changed multiple times within a very short period of time (for same PK), and the respective change tracking process runs for a longer period than the time-frame during which multiple changes for same value occurred, the last value change registered will be recorded, but all prior value changes might not be registered into the respective replica history table. To remidiate the discrepancy, affected tables have to be reseeded (on schedule or manually). In cases with planned fail-over or migration cut-over, reseeding of temporal tables with discrepancies is an important step.
9.2 Prior to version 13.0:
Temporal table schemas are replicated during initial seeding, but data is not automatically migrated as part of the initial seeding. Ongoing changes are registered into temporal tables, maintained by the replica SQL Server.
Important (applicable to both Change Data Capture (CDC) and Change Tracking selected method for tracking of changes):
If a temporal table field value is changed multiple times within a very short period of time (for same PK), and the respective change tracking process runs for a longer period than the time-frame during which multiple changes for same value occurred, the last value change registered will be recorded, but all prior value changes might not be registered into the respective replica history table. To remediate the discrepancy, affected tables have to be reseeded (on schedule or manually). In cases with planned fail-over or migration cut-over, reseeding of temporal tables with discrepancies is an important step.
See option #2 here: https://cloudbasic.net/documentation/configure-rds-sqlserver-alwayson/sql-server-to-sql-server-replication/
A reference in documentation which will help you to get started with RDS backup into S3 and restore from S3: https://cloudbasic.net/documentation/rds-sql-server-backup-restore-s3/
With the fully-automated replication option (see option #1 here https://cloudbasic.net/documentation/configure-rds-sqlserver-alwayson/sql-server-to-sql-server-replication/), the encrypted objects will be skipped. You can add the scripts to the Pre-Seeding Action Script sections of the [Advanced] settings (during initial replication configuration). Or execute those scripts manually against the replica after the seeding completes.
For security reasons, encrypted objects will be excluded from ongoing DDL change tracking.
13. Applicable to replication jobs of the following replica types: S3 Data Lake, Redshift, Snowflake, Azure Synapse, BigQuery, Google CloudSQL and Aurora PostgreSQL :
13.1 Tables only are replicated. Data types mapping is automatically selected.
Note: fully or partially automated replication of views (not applicable to target S3 Data Lake ) is expected to be added in later product versions.
13.2 For SCD Type 2 (tracking of historical changes), with selected method for tracking of changes Change Tracking (Not applicable to CDC), data lake and DWH jobs, it is possible to FAIL TO TRACK intermediate row value changes occurring continuously, especially when the job is configured to Not run continuously. Change Tracking method is allowed for selection, and is the only option for source SQL Server types which do not support CDC (entry editions of Azure SQL, SQL Server Web Edition etc), but CHANGE DATA CAPTURE (CDC) is strongly recommended.
Conversion of job tracking method for existing change tracking jobs, without data loss or the need to rebuild the jobs, is supported . Contact Support for more information.
14. Applicable to replication jobs of the following replica types: Snowflake, Azure Synapse, BigQuery, Google CloudSQL and Aurora PostgreSQL :
14.1 The following SQL Server data types are not tracked for changes (table column data types are mapped to target data types and created on target Snowflake, PostgreSQL, BigQuery/CloudSQL databases as part of schema change tracking, but actual data is not tracked for changes at this point): varbinary, image, geometry, geography, binary, rowversion
14.2 Up to version InterCloud 3.18, if Schema Change tracking is activated, all schema changes except column rename are handled in a fully automated manner. Limitation: a column rename would result into target renamed column drop and recreate, which might result into a partial data loss in certain cases (if the release roll out is not handled properly: i.e. the stream of continuous changes continuous while schema changes are handled), which would require a table reseed (subject to automation, contact Support for more information). Renamed columns should be handled manually up to InterCloud version 3.18. Contact Support form more information. This limitation is expected to be addressed (seamless handling added) in the next incremental release.