-
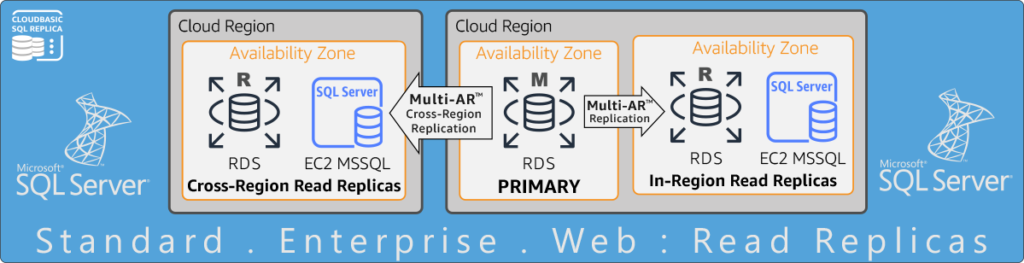
Cross-Region & In-Region Read Replicas for RDS SQL Server Standard, EE & Web
Enable RDS Multi-AR for a more resilient SQL Server cross-region DR strategy.
Safeguard SQL Server against ransomware attacks and human errors. Meet compliance goals.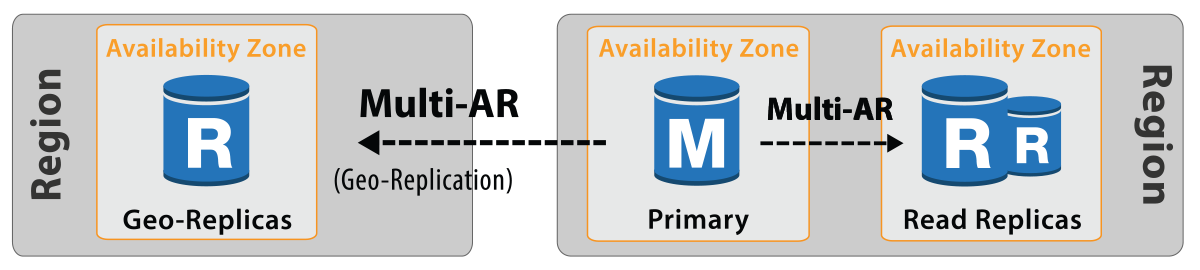
SQL Standard Read Replicas | RDS to EC2 Replicas | Lower TCO | Downgrade to SQL Standard
Working with Read Replicas for MS SQL Server in Amazon RDS
The purpose of using read replicas in Amazon RDS DB instances is for configuring replication for that RDS DB instance.
The following topics will be covered in this section of Read Replicas for Microsoft SQL Server in Amazon RDS:
• Configuring Read Replicas for SQL Server
• Read Replica Limitations with SQL Server
• Troubleshooting a SQL Server Read Replica Problem
Configuring Read Replicas for SQL Server
One of the pre-requisite for setting up DB instance for replication is that the Source DB in Amazon RDS should be in Multi A-Z Deployment mode with Always-On Availability Groups (AGs) and automatic backups also need to be enabled on it. The Multi A-Z deployment will enforce that automatic backups are enabled. Additionally changing the setting of backup retention period to nay value apart from zero will also enable it manually.
The Read replica in Amazon RDS is created by taking a snapshot of the Source DB instance. No Downtime is required for creating the Read Replica or even while deleted the Read Replica. Amazon RDS will configure the settings and the permission for the Source DB without affecting the performance.
The minimum requirement of Read replica is that it should have the same configuration as that of the Source DB and the maximum number of Read Replicas that can be created currently from the Single Source DB instance is five. However this number may change in future. It is recommended to have sufficient compute, network and storage resources for Read replicas while receiving the changes from the source. Hence the Read replica can be configured of higher instance family or better storage capacity as compared to the Source DB instance. Amazon is not responsible and neither intervenes for lagging of replication between source DB and read replica if the Read replica is not loaded with sufficient resources to handle the operational load.
The SQL Server DB engine version of the primary DB instance must be same as that of all the Read Replicas. This is because irrespective of the Maintenance windows that are setup while configuring the RDS instances, Amazon RDS will upgrade the master DB immediately followed by its subsequent Read Replicas.
Read Replica Limitations with SQL Server
- There are certain limitations which exist while working with Read Replicas for SQL Server. The following are its limitations that one needs to consider:-
- Read replicas work only with SQL Server Enterprise Edition (EE) engine.
- Read replicas are available only for SQL Server versions 2016 and 2017.
- Read Replica of Read Replica can be created only for MySQL, PostgreSQL and MariaDB, it is not supported for Oracle and SQL Server.
- The source DB instance needs to be replicated in Multi-AZ deployment with Always-On AGs.
- Read replicas are only available for DB instances on the EC2-VPC platform.
- The DB Instance must belong to a family with at least 4 vCPU to support Read Replicas.
- Read Replicas can be configured only in the same AWS region and not cross region.
- No Backup retention policies can be set for read replicas
- Point-in-time recovery is not possible from read replicas.
- Manual snapshots cannot be taken from read replicas
- Write Operations can be performed on Read Replicas only for MariaDB and MySQL.
- Synchronization of user logins to read replicas is not possible.
- Amazon RDS does not Supports Circular Replication which means that a DB instance cannot serve as the replication source for an existing DB Instance, only new Read Replicas can be created from existing DB Instance. E.g.:- if Database Instance ABC replicates to a Read Replica Instance XYZ then the Read Replica Instance XYZ cannot be used to replicate back to Database Instance ABC.
- The backups in Amazon RDS SQL Server are configured using option groups. The option group for the read replica is same as that of the Source DB Instance. Any changes to the configuration to the option group will be immediately applied to the Source DB Instance irrespective of the Maintenance window and the same will be delegated to the read replicas.
Troubleshooting a SQL Server Read Replica Problem
The replication lag between the Source DB and the Read replica can be monitored using the ReplicaLag metric in Amazon CloudWatch.
If replication lag is too long, the following query can be used for gathering information about the lag:
SELECT AR.replica_server_name
, DB_NAME (ARS.database_id) 'database_name'
, AR.availability_mode_desc
, ARS.synchronization_health_desc
, ARS.last_hardened_lsn
, ARS.last_redone_lsn
, ARS.secondary_lag_seconds
FROM sys.dm_hadr_database_replica_states ARS
INNER JOIN sys.availability_replicas AR ON ARS.replica_id = AR.replica_id
--WHERE DB_NAME (ARS.database_id) = 'database_name'
ORDER BY AR.replica_server_name;
SQL.REPLICA FOR SQL SERVER ON AWS RDS/EC2 & AZURE
CLOUDBASIC for Amazon RDS SQL Server Read Replicas and Disaster Recovery (DR)
Back to Articles Index