-
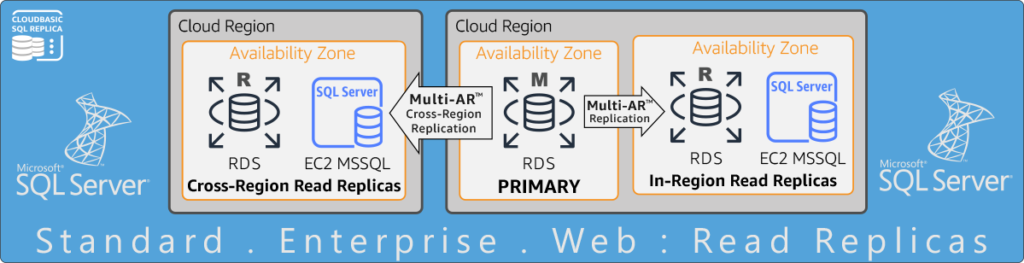
Cross-Region & In-Region Read Replicas for RDS SQL Server Standard, EE & Web
Enable RDS Multi-AR for a more resilient SQL Server cross-region DR strategy.
Safeguard SQL Server against ransomware attacks and human errors. Meet compliance goals.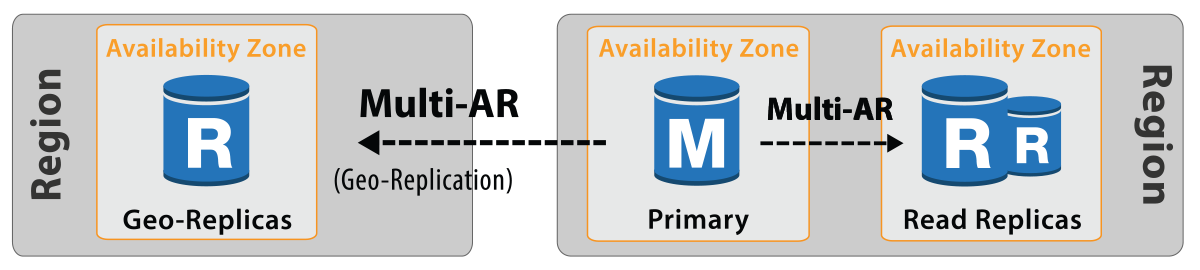
SQL Standard Read Replicas | RDS to EC2 Replicas | Lower TCO | Downgrade to SQL Standard
AWS RDS Read Replicas - Overview
In this article we briefly discuss database replication in the cloud, specifically:
-
-
- RDS
- Read replica
- Read replica business Use Cases
- Provisioning a read replica
- Promoting a read replica to standalone DB instance
- Cross region read replica
- Cost region replication consideration and cost factor
- Read replica monitoring
-
RDS
RDS is a relational database service offered in the cloud by AWS which reduces the operational complexity in running and maintaining database. RDS makes it simple and easy to make relational database in cloud.
Read Replica
Read replica is a special type of RDS database instance which asynchronously syncs up the data from source database instance to replica instances. Read replica database instance is designed to accept only read-only connections, whereas source database instances or master as it is called can accept both write and read connections. Read replica only supports unidirectional replication from source database instances to read database instances.
Read replica business use cases
Read replica is generally preferred in the following scenarios:
Segregate read workloads from write workloads: In a typical enterprise production system there will be use cases to query database on a regular basis for generating intraday and end of day of day reports, generating business intelligence dashboards etc, which puts a toll on database performance if there is a single database instance serving both write and read queries. Setting up read replicas alleviates this concern by dedicating a separate set of database instances for database intensive queries.
Multi region fail over: AWS gives the user the agility to failover workloads from one region to another region in case of a region outage or during a scheduled business continuity exercise. In case of RDS, this is facilitated by provisioning read replicas in a different region i.e. the writer/reader database instance being active in the primary region and read replicas from other regions connected to it to copy data asynchronously. During the time of regional failover, users can convert the read replicas to write database instances in secondary region and write database instances to read in the primary region.
Data Availability: Read replicas helps in serving read queries when the primary database is down. Data in the read replica will be stale at this time due to the issue with primary database, however applications which are querying the database can perform without any downtime.
Reduce latency: Helps in reducing latency in read operation by provisioning read replicas closer to the region where the users access the data.
Provisioning a Read Replica
Read replica can be provisioned by one of the following methods:
• Through AWS console
• Using AWS CLI
• Invoking RDS API
While provisioning a read replica, Amazon takes a DB snapshot of primary database instance and creates the new read replica. Database snapshotting can affect the performance of the master database for a short duration. This is typically avoided in a Multi-AZ RDS deployment where the database snapshot will be created from the stand by instance of RDS hence not affecting the ongoing transactions.
Promoting a read replica to standalone DB instance
There are many scenarios as described in "Business use cases" section to promote a read replica to standalone DB instance. There are few things to keep in mind from an operational standpoint while promoting a read replica to standalone DB instance, which are described below:
Due to the asynchronous nature of copying data from source to read replicas, there will be a replication lag between source DB instance and replica instances hence one should stop all the transactions to source DB instance and wait for the replication lag to be zero before promoting read replica to standalone database instances. There is a CloudWatch metric to monitor the replication lag between source DB instance and replica instances.
Actual promotion of a read replica to stand alone DB instance can be done by performing Promote option on the RDS console or promote-read-replica call from AWS CLI.
Cross region read replica
Creation of cross region read replica is primarily to aid disaster recovery and to reduce read latency to users in different geographies. Steps to create read replica's in another region is similar to creating replica's in the same region, however not all RDS database engines and AWS regions support cross region replication. An example of database engine not supporting cross region replication is Microsoft SQL Server.
Cross region replication consideration and cost factor
• Considerations
Cross region replication is not supported by all RDS database engines. For example SQL server doesn't support cross region replication.
Data from source database can be replicated to multiple read replicas in different AWS regions.
There is latency involved while replicating data from source database region to a read replica in another region.
For encrypting the data in read replica the source database instance needs to be encrypted as well. Encryption of data in RDS is done using KMS which means KMS key should be made available in read replica region for the application to query the data from read replica. Sharing of KMS key is done by enabling cross region access of the KMS key to other region using KMS key policy.
Cross region read replica can be created from a source DB instance which is either in a VPC or outside VPC.
• Cost Factors
Cost associated with cross region transfer is primarily due to the data transfer cost which is involved in replicating the data from one region to another. Pricing for cross region data transfer varies from region to region. There can be few optimisation done to reduce the cost while transferring data from source DB instance to multiple read replicas in the same region. For instance instead of having the data being transferred from the same region to 3 different read replica instances, replication can be optimized by replicating from source DB instance to a single read replica in one region and from that read replica to other read replicas in the same region thus saving on cross region replication data transfer costs.
Read Replica Monitoring
RDS provides various statuses to determine the current state of replication. Here are some of the statuses which are useful while trouble shooting the replication issues:
- REPLICATING
- REPLICATION DEGRADED
- TERMINATED
- ERROR
Using a combination of AWS CloudTrail and CloudWatch events, these status can be alerted and reported to operation teams for the appropriate actions. In addition to the above status provided by RDS, there is a CloudWatch metric named REPLICA LAG which can give a real time view of the replication lag between source DB instance and replica DB instance. This metric can be further plugged into alerting and monitoring mechanism to take appropriate actions.