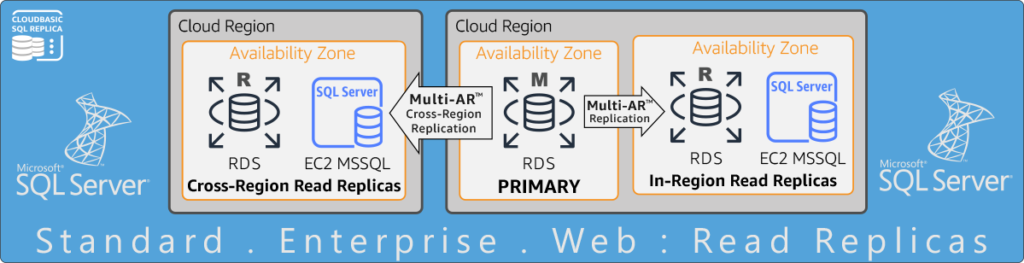
-
Cross-Region & In-Region Read Replicas for RDS SQL Server Standard, EE & Web
Enable RDS Multi-AR for a more resilient SQL Server cross-region DR strategy.
Safeguard SQL Server against ransomware attacks and human errors. Meet compliance goals.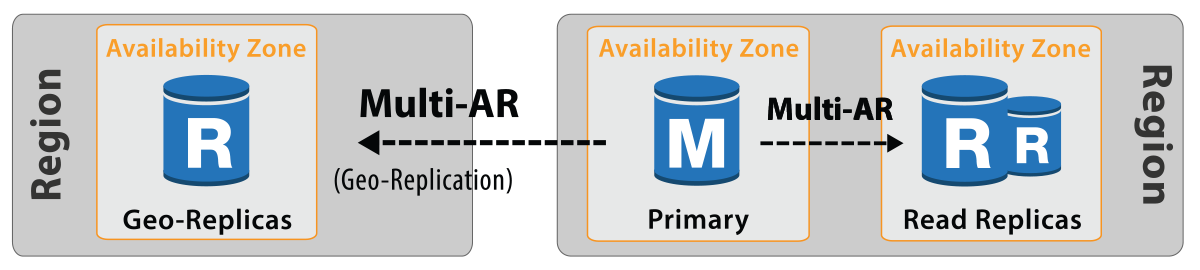
SQL Standard Read Replicas | RDS to EC2 Replicas | Lower TCO | Downgrade to SQL Standard
Microsoft SQL Server on Amazon RDS
Amazon RDS supports DB instances running several versions and editions of Microsoft SQL Server. The following list of Microsoft SQL Server are supported for Amazon RDS. If no version is specified, Amazon RDS defaults to a supported version, typically the most recent version. If a major version is specified but a minor version is not, Amazon RDS defaults to a recent release of the major version you have specified.
| Major Version | Minor Version | RDS API Engine Version and CLI engine-version |
| SQL Server 2017 | 14.00.3281.6 (CU19)
14.00.3223.3 (CU16) 14.00.3192.2 14.00.3049.1 14.00.3035.2 (CU9 GDR) 14.00.3015.40 (CU3) 14.00.1000.169 (RTM) |
14.00.3281.6.v1
14.00.3223.3.v1 14.00.3192.2.v1 14.00.3049.1.v1 14.00.3035.2.v1 14.00.3015.40.v1 14.00.1000.169.v1 |
| SQL Server 2016 | 13.00.5598.27 (SP2 CU11)
13.00.5426.0 (SP2 CU8) 13.00.5366.0 (SP2) 13.00.5292.0 (CU6) 13.00.5216.0 (CU3) 13.00.4522.0 (SP1 CU10 Security Update) 13.00.4466.4 (SP1 CU7) 13.00.4451.0 (SP1 CU5) 13.00.4422.0 (SP1 CU2) 13.00.2164.0 (RTM CU2) |
13.00.5598.27.v1
13.00.5426.0.v1 13.00.5366.0.v1 13.00.5292.0.v1 13.00.5216.0.v1 13.00.4522.0.v1 13.00.4466.4.v1 13.00.4451.0.v1 13.00.4422.0.v1 13.00.2164.0.v1 |
| SQL Server 2014 | 12.00.6329.1 (SP3 CU4)
12.00.6293.0 (SP3 CU3) 12.00.5571.0 (SP2 CU10) 12.00.5546.0 (SP2 CU5) 12.00.5000.0 (SP2) |
12.00.6329.1.v1
12.00.6293.0.v1 12.00.5571.0.v1 12.00.5546.0.v1 12.00.5000.0.v1 |
| SQL Server 2012 | 11.00.7493.4 (SP4 GDR)
11.00.7462.6 (SP4 GDR) 11.00.6594.0 (SP3 CU8) 11.00.6020.0 (SP3) 11.00.5058.0 (SP2), except US East (Ohio), Canada (Central), and Europe (London) |
11.00.7493.4.v1
11.00.7462.6.v1 11.00.6594.0.v1 11.00.6020.0.v1 11.00.5058.0.v1 |
Amazon RDS helps you to create DB Instances, snapshots, point-in-time restores, automated or manual backups as well. Amazon RDS currently supports Multi-AZ deployments for SQL Server using SQL Server Database Mirroring (DBM) or Always-On Availability Groups (AGs) as a high-availability, failover solution.
Since Amazon RDS is a fully managed Database instance, there is no admin access granted to the shell of the DB engine which restricts access to certain system procedures and tables that requires advanced privileges. Instead of that master user is provided to the db_owner role for all user databases which are created within the Amazon RDS Instance. Amazon RDS does not allow direct host access to a DB instance via Telnet, Secure Shell (SSH), or Windows Remote Desktop Connection. Amazon RDS manages the backups so the master user does not has rights to take backups on its own.
Version Management in Amazon RDS
Amazon RDS includes flexible version management that enables to control when and how the DB instance is patched or upgraded. This enables to perform the following action on the DB Instance:-
• Maintain compatibility with database engine patch versions.
• Test new patch versions to verify that they work with the application before deploying them in production.
• Plan and perform version upgrades to meet SLAs.
Microsoft SQL Server Engine Patching in Amazon RDS
Amazon RDS periodically aggregates official Microsoft SQL Server database patches into a DB instance engine version that's specific to Amazon RDS.
Common Management Tasks for Microsoft SQL Server on Amazon RDS
Below is the list of common configurations that needs to be specified while creating Amazon RDS SQL Server DB Instance:
1. Amazon RDS supports only specific type of Instance class which corresponds to specific CPU and RAM settings. A particular instance class, storage type and Provisioned IOPS details needs to be specified.
2. The database instance during the creation can be setup in Multi A-Z Deployment mode to provide increased availability, data durability and fault tolerance.
3. The RDS instance can be spinned up in default VPC or in a user created VPC which needs to be created before creating the instance and also its respective subnets.
4. By default, DB instances are created with a firewall that prevents access to them. Hence appropriate rules needs to be defined on the security groups.
5. The parameter groups needs to be defined so that the DB Instance will be created with those specific set of parameters and option groups.
6. After creating the security group and associating it with the DB Instance, the Amazon RDS SQL Server can be accessed using any standard SQL Client application like SSMS, CMD.
7. Amazon RDS takes care of automatic backups, however the maintenance and the backup windows can be specified. Also manually backup and restore operations can also be performed using the full backup files but there are limitations as well around it.
8. Some of the other optional configurations are enabling of CloudWatch metrics, events, log Files and enhanced monitoring.
Limitations for Microsoft SQL Server DB Instances
Below are some of the limitations while working with Amazon RDS SQL Server:
1. The maximum number of databases supported on a DB instance depends on the instance class type and the availability mode—Single-AZ, Multi-AZ Database Mirroring (DBM), or Multi-AZ Availability Groups (AGs). The system databases are not counted in this limit.
The following table shows the maximum number of supported databases for each instance class type and availability mode. The table will also be helpful in determining whether a instance can be moved from one instance class type or one from one availability zone to another. If the source DB instance has more databases than the target instance class type then the modification of the database fails.
| Instance Class Type | Single-AZ | Multi-AZ with DBM | Multi-AZ with Always On AGs |
| db.*.micro to db.*.medium | 30 | N/A | N/A |
| db.*.large | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| db.*.xlarge to db.*.16xlarge | 100 | 50 | 75 |
| db.*.24xlarge | 100 | 50 | 100 |
* Represents the different instance class types. E.g.:- m4, m5, r4, r5
For example, if the DB instance runs on a db.*.16xlarge with Single-AZ and that it has 76 databases and if the modification request is to upgrade to using Multi-AZ with Always-On (AGs) then the upgrade will fail, because the DB instance contains more databases than the target configuration can support. If modification request is to upgrade the instance class type to db.*.24xlarge instead, the modification succeeds.
If the upgrade fails, the events and messages are similar to the following:
Unable to modify database instance class. The instance has 76 databases, but after conversion it would only support 75.
2. Some ports are reserved for Amazon RDS, and those cannot be used while creating the DB Instance.
3. Client connections from IP addresses within the range 169.254.0.0/16 are not permitted. This is the Automatic Private IP Addressing Range (APIPA), which is used for local-link addressing.
4. SQL Server Standard Edition will use only a subset of the available processors if the DB instance has more processors than the software limits (24 cores, 4 sockets, and 128GB RAM).
5. Amazon RDS for SQL Server doesn't support importing data into the msdb database.
6. The databases cannot be renamed on a DB instance in a SQL Server Multi A-Z Deployment.
7. The maximum storage size for SQL Server DB instances is the following:
• General Purpose (SSD) storage – 16 TiB for all editions
• Provisioned IOPS storage – 16 TiB for all editions
• Magnetic storage – 1 TiB for all editions
8. The minimum storage size for SQL Server DB instances is the following:
• General Purpose (SSD) storage – 20 GiB for Enterprise, Standard, Web, and Express editions
• Provisioned IOPS storage – 20 GiB for Enterprise and Standard editions, 100 GiB for Web and Express editions
• Magnetic storage – 200 GiB for Enterprise and Standard editions, 20 GiB for Web and Express editions
9. Amazon RDS doesn't support running these services on the same server as your Amazon RDS DB instance:
• SQL Server Integration Services
• SQL Server Reporting Services
• Data Quality Services
• Master Data Services
10. Because of limitations in Microsoft SQL Server, restoring to a point in time before successful execution of DROP DATABASE might not reflect the state of that database at that point in time.
11. For SQL Server, you create your databases after you create your DB instance. Database names follow the usual SQL Server naming rules with the following differences:
• Database names can't start with rdsadmin.
• They can't start or end with a space or a tab.
• They can't contain any of the characters that create a new line.
DB Instance Class Support for Microsoft SQL Server
The computation and memory capacity of a DB instance is determined by its DB instance class. The DB instance class you need depends on your processing power and memory requirements
The following list of DB instance classes supported for Microsoft SQL Server:
• They can't contain a single quote (').
| QL Server Edition | 2017 and 2016 Support Range | 2014 and 2012 Support Range |
| Enterprise Edition | db.t3.xlarge–db.t3.2xlarge
db.r3.xlarge–db.r3.8xlarge db.r4.xlarge–db.r4.16xlarge db.r5.xlarge–db.r5.24xlarge db.m4.xlarge–db.m4.16xlarge db.m5.xlarge–db.m5.24xlarge db.x1.16xlarge–db.x1.32xlarge db.x1e.xlarge–db.x1e.32xlarge db.z1d.xlarge–db.z1d.3xlarge |
db.t3.xlarge–db.t3.2xlarge
db.r3.xlarge–db.r3.8xlarge db.r4.xlarge–db.r4.8xlarge db.r5.xlarge–db.r5.24xlarge db.m4.xlarge–db.m4.10xlarge db.m5.xlarge–db.m5.24xlarge db.x1.16xlarge–db.x1.32xlarge db.x1e.xlarge–db.x1e.32xlarge |
| Standard Edition | db.t3.xlarge–db.t3.2xlarge
db.r4.large–db.r4.16xlarge db.r5.large–db.r5.24xlarge db.m4.large–db.m4.16xlarge db.m5.large–db.m5.24xlarge db.x1.16xlarge–db.x1.32xlarge db.x1e.xlarge–db.x1e.32xlarge db.z1d.large–db.z1d.3xlarge |
db.t3.xlarge–db.t3.2xlarge
db.r3.large–db.r3.8xlarge db.r4.large–db.r4.8xlarge db.r5.large–db.r5.24xlarge db.m3.medium–db.m3.2xlarge db.m4.large–db.m4.10xlarge db.m5.large–db.m5.24xlarge db.x1.16xlarge–db.x1.32xlarge db.x1e.xlarge–db.x1e.32xlarge |
| Web Edition | db.t2.small–db.t2.medium
db.t3.small–db.t3.2xlarge db.r4.large–db.r4.2xlarge db.r5.large–db.r5.4xlarge db.m4.large–db.m4.4xlarge db.m5.large–db.m5.4xlarge db.z1d.large–db.z1d.3xlarge |
db.t2.small–db.t2.medium
db.t3.small–db.t3.2xlarge db.r3.large–db.r3.2xlarge db.r4.large–db.r4.2xlarge db.r5.large–db.r5.4xlarge db.m3.medium–db.m3.2xlarge db.m4.large–db.m4.4xlarge db.m5.large–db.m5.4xlarge |
| Express Edition | db.t2.micro–db.t2.medium
db.t3.small–db.t3.xlarge |
db.t2.micro–db.t2.medium
db.t3.small–db.t3.xlarge |
Microsoft SQL Server Security
The Microsoft SQL Server database engine uses role-based security. The master user name used while creating a DB instance is a SQL Server Authentication login that is a member of the processadmin, public, and setupadmin fixed server roles. Any user who creates a database is assigned to the db_owner role for that database and has all database-level permissions except for those that are used for backups.
The following server-level roles are not currently available in Amazon RDS:
• bulkadmin
• dbcreator
• diskadmin
• securityadmin
• serveradmin
• Sysadmin
The following server-level permissions are not available on SQL Server DB instances:
• ALTER ANY CREDENTIAL
• ALTER ANY EVENT NOTIFICATION
• ALTER ANY EVENT SESSION
• ALTER RESOURCES
• ALTER SETTINGS ( Instead use DB parameter group API operations to modify parameters)
• AUTHENTICATE SERVER
• CONTROL_SERVER
• CREATE DDL EVENT NOTIFICATION
• CREATE ENDPOINT
• CREATE TRACE EVENT NOTIFICATION
• EXTERNAL ACCESS ASSEMBLY
• SHUTDOWN ( Use the RDS reboot option instead)
• UNSAFE ASSEMBLY
• ALTER ANY AVAILABILITY GROUP (SQL Server 2012 only)
• CREATE ANY AVAILABILITY GROUP (SQL Server 2012 only)
Compliance Program Support for Microsoft SQL Server DB Instances
HIPAA Support for Microsoft SQL Server DB Instances
Amazon RDS for SQL Server supports HIPAA for the following versions and editions:
• SQL Server 2017 Enterprise, Standard, and Web Editions
• SQL Server 2016 Enterprise, Standard, and Web Editions
• SQL Server 2014 Enterprise, Standard, and Web Editions
• SQL Server 2012 Enterprise, Standard, and Web Editions
To enable HIPAA support on your DB instance, set up the following three components.
| Component | Details |
| Auditing | To set up auditing, set the parameter rds.sqlserver_audit to the value fedramp_hipaa. If the DB instance is not already using a custom DB parameter group, then a custom parameter group needs to be created and attach it to the DB instance before modifying the rds.sqlserver_audit parameter. |
| Transport Encryption | To set up transport encryption, force all connections to the DB instance to use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). |
| Encryption at Rest | To set up encryption at rest, there are two options:-
If the DB is running on Enterprise Edition then Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) can be used to achieve encryption at rest. Encryption at rest can also set by using AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) encryption keys. |
SSL is supported in all AWS Regions and for all supported SQL Server editions.
Microsoft SQL Server Features on Amazon RDS
The supported SQL Server versions on Amazon RDS include the following features.
Microsoft SQL Server 2017 Features
SQL Server 2017 includes many new features, such as the following:
• Adaptive query processing
• Automatic plan correction
• GraphDB
• Resumable index rebuilds
Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Features
Amazon RDS supports the following features of SQL Server 2016:
• Always Encrypted
• JSON Support
• Operational Analytics
• Query Store
• Temporal Tables
Microsoft SQL Server 2014 Features
In addition to supported features of SQL Server 2012, Amazon RDS supports the new query optimizer available in SQL Server 2014, and also the delayed durability feature. SQL Server 2014 supports all the parameters from SQL Server 2012 and uses the same default values. SQL Server 2014 includes one new parameter, backup checksum default.
Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Features
In addition to supported features of SQL Server 2008 R2, Amazon RDS supports the following SQL Server 2012 features:
• Columnstore indexes (Enterprise Edition)
• Online Index Create, Rebuild and Drop for XML, varchar(max), nvarchar(max), and varbinary(max) data types (Enterprise Edition)
• Flexible Server Roles
• Service Broker is supported, Service Broker endpoints are not supported
• Partially Contained Databases
• Sequences
• Transparent Data Encryption (Enterprise Edition only)
• THROW statement
• New and enhanced spatial types
• UTF-16 Support
• ALTER ANY SERVER ROLE server-level permission
Change Data Capture Support for Microsoft SQL Server DB Instances
Amazon RDS supports change data capture (CDC) for the DB instances running Microsoft SQL Server. CDC captures changes that are made to the data in tables, and stores metadata about each change that which can be accessed later.
Amazon RDS supports CDC for the following SQL Server editions and versions:
• Microsoft SQL Server Enterprise Edition (All versions)
• Microsoft SQL Server Standard Edition:
- 2017
- 2016 version 13.00.4422.0 SP1 CU2 and later
To use CDC with Amazon RDS DB instances, first enable or disable CDC at the database level by using RDS-provided stored procedures. After that, any user that has the db_owner role for that database can use the native Microsoft stored procedures to control CDC on that database. CDC and AWS Database Migration Service can be used to enable ongoing replication from SQL Server DB instances.
Features Not Supported and Features with Limited Support
The following Microsoft SQL Server features are not supported on Amazon RDS:
• Backing up to Microsoft Azure Blob Storage
• Buffer pool extension
• Data Quality Services
• Database Log Shipping
• Database Mail
• Extended stored procedures, including xp_cmdshell
• FILESTREAM support
• File tables
• Machine Learning and R Services (requires OS access to install it)
• Maintenance Plans
• Performance Data Collector
• Policy-Based Management
• PolyBase
• Replication
• Resource Governor
• Server-level triggers
• Service Broker endpoints
• Stretch database
• T-SQL endpoints (all operations using CREATE ENDPOINT are unavailable)
• WCF Data Services
The following Microsoft SQL Server features have limited support on Amazon RDS:
• Distributed Queries / Linked Servers.
Multi-AZ Deployments Using Microsoft SQL Server Database Mirroring or Always On Availability Groups
Amazon RDS supports Multi-AZ deployments for DB instances running Microsoft SQL Server by using SQL Server Database Mirroring (DBM) or Always-On Availability Groups (AGs).Multi-AZ deployments provide increased availability, data durability, and fault tolerance for DB instances. In the event of planned database maintenance or unplanned service disruption, Amazon RDS automatically fails over to the up-to-date secondary replica so database operations can resume quickly without manual intervention. The primary and secondary instances use the same endpoint, whose physical network address transitions to the passive secondary replica as part of the failover process. The application does not needs to be reconfigured when the failover occurs.
Amazon RDS manages failover by actively monitoring the Multi-AZ deployment and initiating a failover when a problem occurs with the primary. Failover doesn't occur unless the standby and primary are fully in sync. Amazon RDS actively maintains the Multi-AZ deployment by automatically repairing unhealthy DB instances and re-establishing synchronous replication. No manual intervention is required to manage it. Amazon RDS handles the primary, the witness, and the standby instance. When SQL Server is setup in Multi-AZ, RDS configures passive secondary instances for all of the databases on the instance.
Amazon RDS supports Microsoft SQL Server Transparent Data Encryption (TDE), which transparently encrypts stored data. Amazon RDS uses option groups to enable and configure these features.
Local Time Zone for Microsoft SQL Server DB Instances
The time zone of an Amazon RDS DB instance running Microsoft SQL Server is set by default. The current default is Universal Coordinated Time (UTC). The time zone for the DB instance can be specified instead of the local time zone to match it with the application Time zone. Even after the failover process has occurred when the RDS DB instance is part of Multi A-Z deployment then there is no change in the time zone after failover.
The following are limitations to setting the local time zone on the DB instance:
• The time zone cannot be modified of an existing SQL Server DB instance.
• The snapshot from a DB instance in one time zone cannot be restored to a DB instance in a different time zone.
Important Note: Always consult the official documentation for Amazon RDS and MS SQL Server, as the notes above may have become outdated.
SQL.REPLICA FOR SQL SERVER ON AWS RDS/EC2 & AZURE
CLOUDBASIC for Amazon RDS SQL Server Read Replicas and Disaster Recovery (DR)
Back to Articles Index